Categorizing pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms (PNENs) based on molecular analysis could aid patient stratification and treatment. In a study published by Cell Reports, four subtypes of PNENs are identified through transcriptome analysis, proteome profiling and whole-genome sequencing.
Pancreatic Cancer
Pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms (PNENs) are malignant tumors that arise from clusters of islet cells—the part of the pancreas responsible for releasing hormones into the blood stream. In addition to being a rare type of pancreatic cancer, many PNENs have unique clinical and biological features that make it difficult to treat.
PNEN Categorization
Clinically, PNENs are broadly categorized as being either functional (they secrete hormone) or nonfunctional (they do not secrete hormone) based on the presenting symptoms. Histological examination of the tumor itself further classifies PNENs into well-differentiated and poorly differentiated. Both systems are used to predict prognosis and guide treatment with varying results.
Past attempts to subdivide PNENs based on molecular features—such as germline and somatic mutations, gene expression profiles, altered signal pathways, chromosome abnormalities and epigenetic studies—have been limited to subsets of PNENs based on histological and/or functional status. In addition, the protein profile of different PNEN subtypes remained largely unexplored.
Molecular Analysis
To classify PNENs based on thorough molecular analysis, a team led by Dr. Sharon Gorski combined data from RNA-sequencing, proteomic profiling and whole exome sequencing. Using 84 PNEN specimens—a random sample not selected by clinical or histological features—they identified four subgroups of PNENs with unique molecular properties.
The four subgroups are outlined below in a diagram published with the paper.
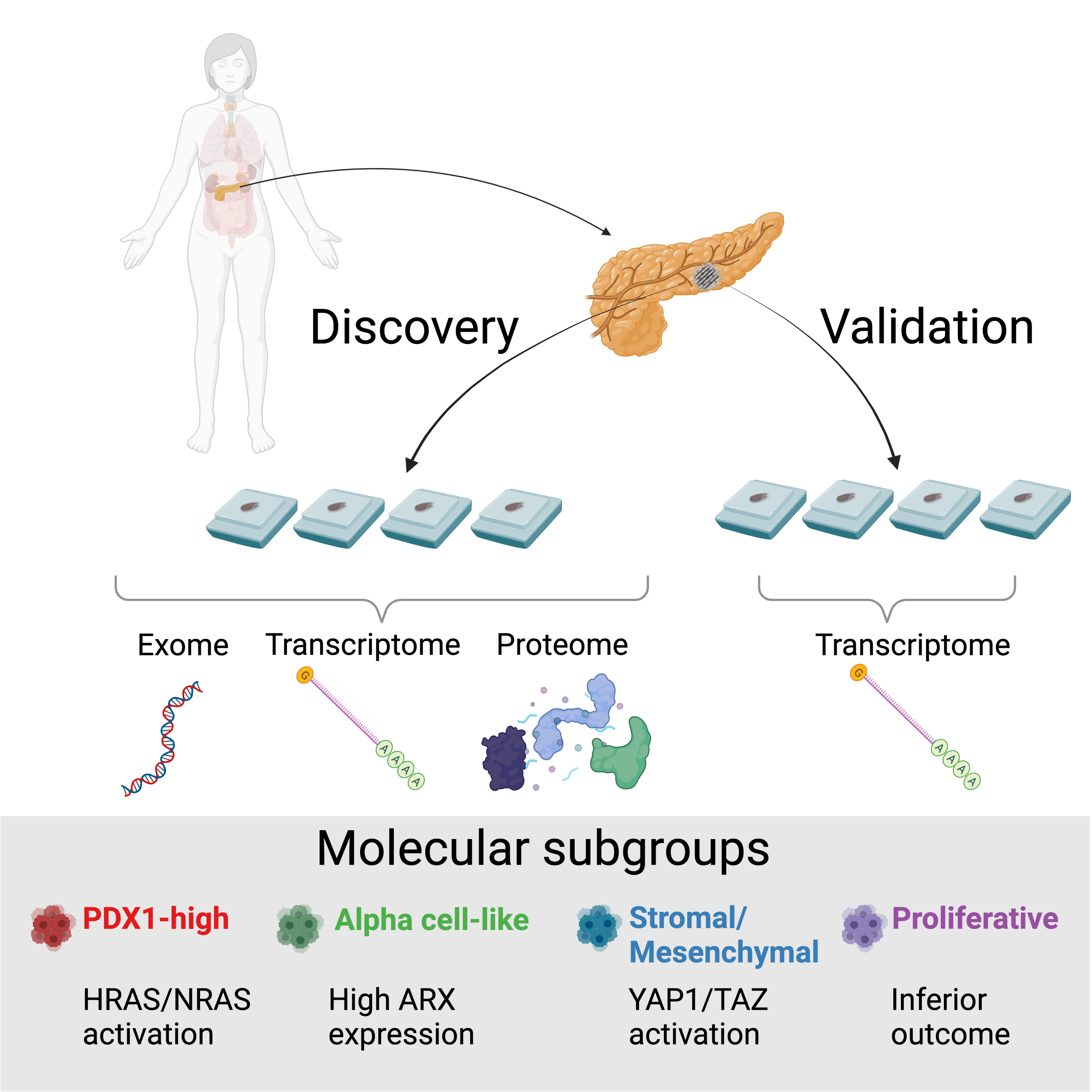
“One of our key findings was a Proliferative subgroup consisting of both well-differentiated and poorly differentiated PNENs,” says Dr. Kevin Yang, the first author of the study. Since well-differentiated and poorly differentiated PNENs are currently managed differently, these results suggest that the classification system should be re-visited with potential implications on clinical practice.

“Another key finding was a Stromal/Mesenchymal subgroup with Hippo pathway involvement, which had never been implicated in PNENs,” says Dr. Yang. “Hippo pathway is an emerging subject in several other cancer types, and its involvement in a subgroup of PNENs provides evidence supporting the potential oncogenic roles of the pathway in PNENs as well as a potential novel avenue for therapeutic intervention that may be beneficial to a population of patients.”
Potential Impact
According to Dr. Yang, two potential areas of further research have emerged from the study findings. One is to identify potential biomarkers that can be incorporated into current clinical practice. The other is to establish the oncogenic roles of select subgroup-specific molecular features.
The information from this study provides a basis for potential stratification of patients with PNENs with therapeutic implications. “The end goals are to help clinical decision making,” says Yang, “and to identify potential therapeutic vulnerabilities of the subgroups for effective treatments.”
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Neuroendocrine Tumor Research Foundation and the Pancreas Centre BC IDEAS Grant.
Image created with BioRender.com
Learn more
Learn more about Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Neoplasms through NORD.
Learn more about Pancreas Centre BC and their efforts to support research that can rapidly translate into better treatment.
For more information about research being done at the GSC, please visit the website for Dr. Sharon Gorski’s lab.
Citation
Kevin C. Yang, Steve E. Kalloger, John J. Aird, Michael K.C. Lee, Christopher Rushton, Karen L. Mungall. Andrew J. Mungall, Dongxia Gao, Christine Chow, Jing Xu, Joanna M. Karasinska, Shane Colborne, Steven J.M. Jones, Jörg Schrader, Ryan D. Morin, Jonathan M. Loree, Marco A. Marra, Daniel J. Renouf, Gregg B. Morin, David F. Schaeffer, Sharon M. Gorski (2021) Proteotranscriptomic classification and characterization of pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms. Cell Reports, 37( 2).
*bold font indicates members of the GSC.